Ecology 203, Fall 1998. Final Exam.
I will not discuss this exam with anyone who has not taken it.
Signed: _____________________________________ Section _______
Multiple Choice (2 points each). Answer all. Expect to spend about 45 minutes here.
Please take your time!
- Primary productivity is usually measured as
- the number of animals in the community
- the number of organisms the community supports
- the mass of the plants in the community
- the height of the vegetation
- Net primary productivity equals
- the difference between gross and raw productivity
- negative and positive photosynthesis
- primary consumption minus primary productivity
- gross primary productivity minus respiration
- Competition generally occurs most intensely between
- members of the same species
- members of related bud different species
- members of unrelated species
- none of the above
- CAM photosynthetic pathway is used by
- chemosynthetic bacteria
- animals in the high arctic
- cacti
- deciduous trees under heat stress
 Plant productivity, at least in many
terrestrial ecosystems, is positively correlated with
Plant productivity, at least in many
terrestrial ecosystems, is positively correlated with
- herbivore consumption
- herbivore biomass
- herbivore productivity
- all of the above
- none of the above
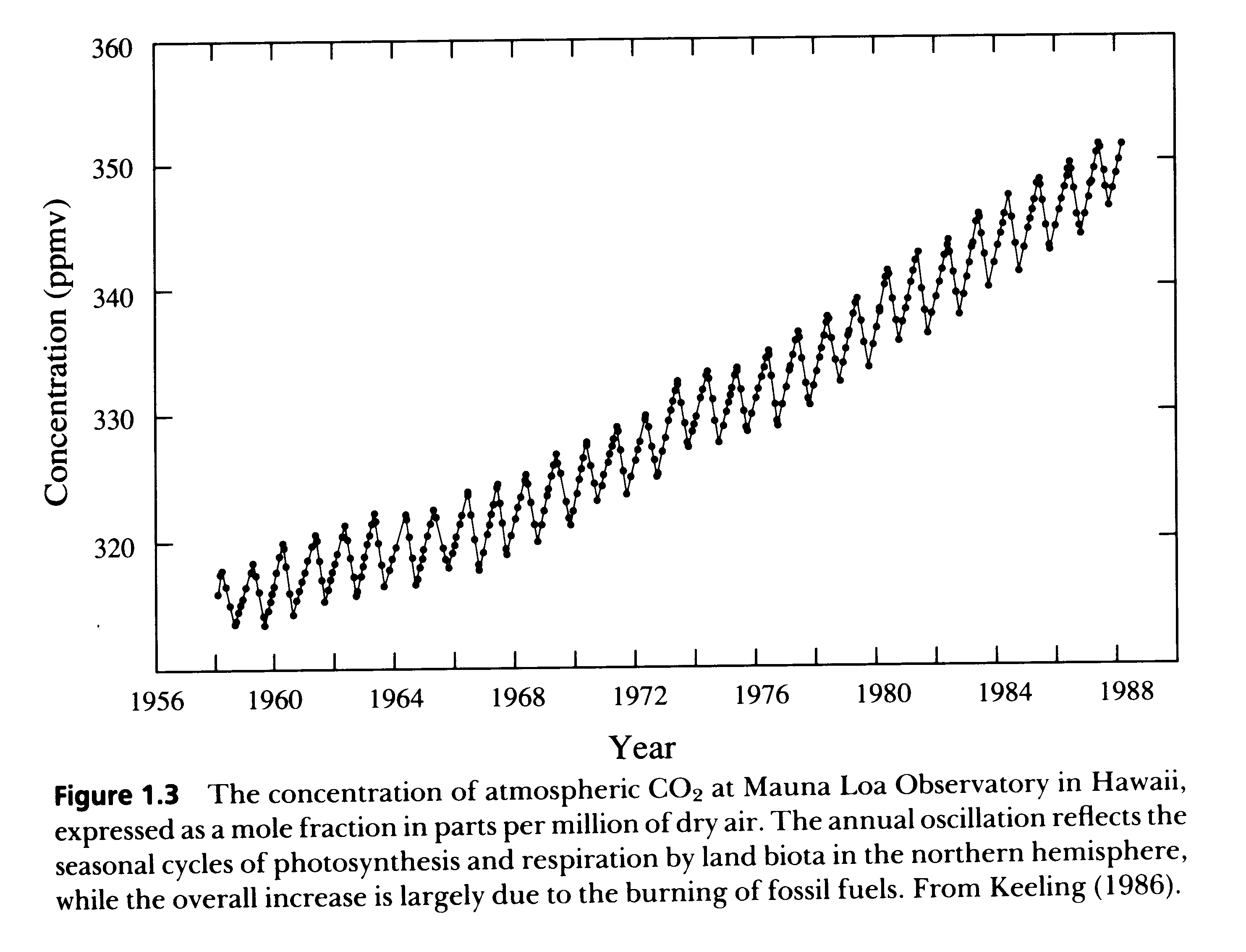
- The figure shows a steady increase in
- the number of gypsy moth caterpillars
- atmospheric CO2
- sulfate released from hydrothermal vent ecosystems
- nitrate input into the Hubbard Brook ecosystem
- The research at Hubbard Brook experimental forest in New Hampshire provides good
evidence that
- acid rain negatively affects stream ecosystems
- biogeochemical processes change little in forests over time
- deforestation alters biogeochemical processes
- global warming is likely to impact forests
- Leaf litter decomposition rates
- increase with increasing latitude
- decrease with increasing moisture
- increase with increasing nitrogen content
- all of the above
- none of the above
- An autotroph is
- an animal that finds its own food
- an organism that makes its own sugars
- an organism that moves around freely (without roots)
- all of the above
- The following are examples of omnivores:
- cat, dog, wolf
- tree, shrub, fern
- human, bird, deer
- raccoon, human, lobster
- According to the 1960 paper by Hairston, Smith, and Slobodkin, the following factor(s)
regulate herbivore populations:
- food (therefore, competition)
- predators
- disease
- density-independent factors
- all of the above
- To fully determine food-web links you should, if possible
- observe everything that organisms actually eat
- determine isotope levels in predator and prey tissues
- conduct removal experiments to see how remaining organisms respond
- all of the above
- none of the above
- The graph suggests that biomes
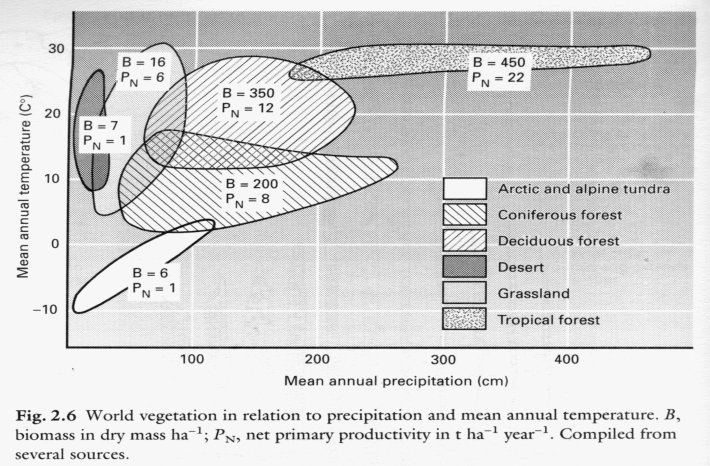 can be separated by temperature
can be separated by temperature- can be separated by precipitation
- can be separated only by both
factors simulataneously
- cannot be separated
- When trying to conserve a population (reduce its chance of going extinct) it is best to
set up a preserve where the population
- functions as a metapopulation
- is as large as possible
- is regulated by density-independent factors
- has all predators removed
- Higher latitudes (both north & south) are colder than lower latitudes (near equator)
because
- of El Niņo
- ice makes it cold
- the circulation of the Earth’s atmosphere brings air from the tropics
- the angle of the sunlight decreases at higher latitudes
- the atmosphere is thinner at higher latitudes
- Regulation of populations due to flooding represents what type of regulation:
- density-dependent regulation
- facultative apomictic regulation
- density-independent regulation
- extrinsic, biotic regulation
- none of the above
- An example of a physiological tradeoff is
- plants grow more slowly when eaten
- plants have to reproduce before they die
- plants have to grow and reproduce
- plants both grow and die
- An organism's fundamental niche is usually
- broader than its realized niche
- more narrow than its realized niche
- more important than its abiotic environment
- none of the above
- Theodosius Dobzhansky once said that nothing in biology makes sense except in the light
of
- ecological complexity
- the sun
- evolution
- antagonistic pleiotropy
- God
- The classic example of hare and lynx populations oscillating, as discussed in lecture
and not in the book, suggests
- hare consumption of lynx varies over time
- ecological systems are not always complicated
- we should be careful about interpreting data
- all of the above
- Frank Egler, rebel ecologist, provided probably the best model of community development
over time. This was the
- initial floristic composition model.
- relay floristics model.
- idea of natural selection.
- individualistic concept.
- Small populations are at risk of going extinct because
- individuals have difficulty finding each other (Allee effect)
- homozygosity increases
- inbreeding increases
- all of the above
- non of the above
True/False. Fill in "A" for TRUE, "B" for FALSE ON ANSWER SHEET.
If the statement is true it will be true under all possible conditions that fall within
the scope of the statement. If it is true most of the time but false occasionally, the
statement is false. If you think the statement seems incomplete then it is probably false.
I recommend graphing, if possible, any statements you find confusing. Answer all. Take a
half hour. (2 points each)
- Frederic Clements believed that communities develop over time just like individual
organisms develop over time.
- Plant productivity is influenced by the amount of solar radiation reaching the leaves.
- C4 photosynthesis yields a four carbon molecule while C3 yields a three carbon molecule
- Plants increase photosynthetic efficiency with decreasing water levels.
- Tropical forests, on average, have higher net primary productivity rates per unit area
than oceans.
- The huge amount of land area, high solar input, and low cloud cover allow deserts to
have gross primary productivity rates that are nearly twice the rates of tropical forests.
- The Sustainable Biosphere Initiative (SBI) is a call for ecologists to not only conduct
basic research but also to get involved with public education and management decisions
regarding ecological systems.
- Only about 25% of the radiation reaching a boreal forest canopy actually makes it to the
forest floor.
- Despite its ill effects on worldwide climate, the warming of the equatorial Pacific
waters (El Niņo) increases that area’s phytoplanktonic productivity.
- Biogeochemical cycles are miss-named because it actually is energy that cycles through
ecosystems.
- The level of herbivore damage to leaves can influence the rate at which those leaves
decompose.
- The amount of biomass in trophic levels, starting from producers and going up through
consumers, looks like a pyramid, with the greatest amount of biomass found in producers
and the least amount of biomass found in predators.
- Time to extinction generally increases with increasing population size.
- Populations growing exponentially can, despite this growth, exhibit a stable age
distribution.
- During forest succession tree volume and biomass increase while the number of trees
decreases, a relationship referred to as both the "self-thinning law" and the
"-3/2 law."
- Shelford’s "law of tolerance" suggests that species go extinct as quickly
as new species arise through evolution.
- When populations are modeled using the "logistic equation" the number of
organisms starts off increasing exponentially but then levels off to a stable equilibrium.
(Recall the lecture on this.)
- Competitive ability and colonization ability are usually inversely related (i.e., form a
tradeoff).
Short answers. Answer the following 4 questions to the best of your ability. Be sure
your answers are complete. Allocate about 15 minutes each. Plan before you
write! (5 points each)
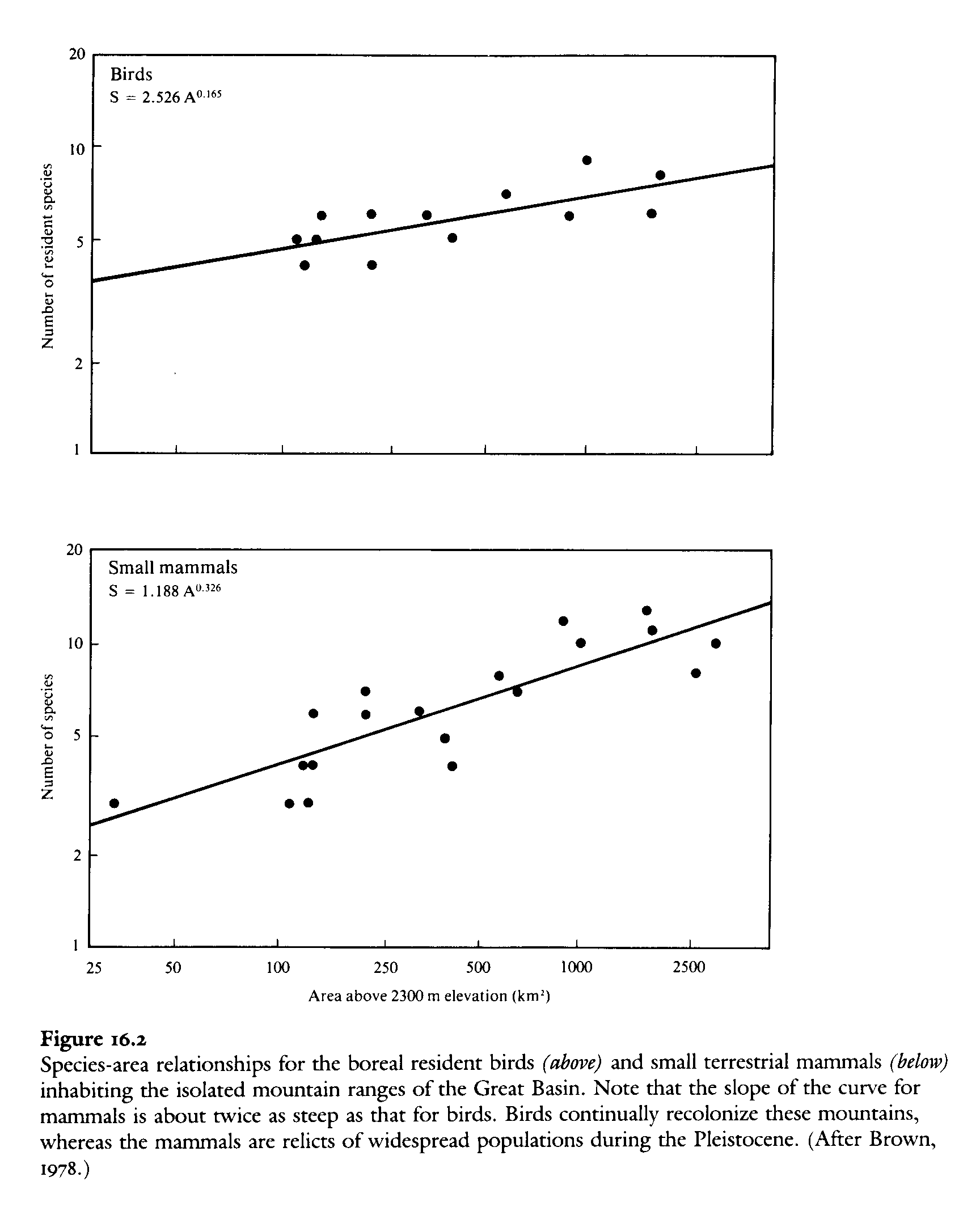
1. The two graphs represent the number
of species of birds (top) and mammals (bottom) on
mountain tops in the Great Basin. Interpret the
significance of the graph. Axes are the same in
both graphs. The equations are not very important
since axes' units are the same. The y-axes show the
number of resident species; the x-axes show the
area above 2300 m.
2. Natural selection is the most important mechanism of evolution, leading to long-term
changes in species over time and to short-term species adaptation to changing
environments. Briefly, but completely, identify and describe the four basic
characteristics of natural selection that Darwin observed and that you can observe.
3. Why should we give a hoot about human-induced climate change?
4. Present a question that you think is challenging enough to ask on this Ecology final
exam. Then answer it. You will be evaluated on the creativity of your question and how
well you answer it. Make it fit in the space provided (e.g., don’t "ask" to
discuss the meaning of life). Take your time!
 Plant productivity, at least in many
terrestrial ecosystems, is positively correlated with
Plant productivity, at least in many
terrestrial ecosystems, is positively correlated with can be separated by temperature
can be separated by temperature