 1. In the figure
1. In the figureEcology 203, Exam I. February 21, 2000 Name ______________________________ (1 pt, spelling counts)
Rules:
Read carefully, work accurately and efficiently. Answer questions to the best of your ability. You usually have a choice. [SS] = student submitted question. Good luck!Multiple Choice. Answer 10. Then circle the number of the question you want evaluated (else I will evaluate the first 10 answered). (3 pts each; 30 pts total)
1. The Hardy-Weinberg Law represents
a. genetic change in a population over time
b. evolutionary change in a population
c. an alternative hypothesis to evolution
d. a null hypothesis for evolution
e. all of the above
2. The change in seasons is due to:
3. Higher latitudes (both north & south) are colder than lower latitudes (near equator) because
4. Evolution, the change in gene frequencies over time, occurs by:
5. Asking "why do lions hunt in packs" best fits within which subdiscipline within ecology:
a. quantitative ecology
b. behavioral ecology
c. population ecology
d. evolutionary ecology
e. community ecology
6. Which of the following is not a "learning objective" of this course:
a. To understand how the process of science operates and how it is used to understand how organisms interact with each other and their environment.
b. To understand how the process of evolution operates and how it influences the dynamics of ecological systems.
c. To be able to critically analyze biological data, both in a statistical sense and in graphical forms.
d. To be able to understand how people's belief in evolution is increased through science.
e. To appreciate how large scale patterns in populations, communities, and ecosystems are influenced by small scale interactions among individuals and between individuals and their local environment.
7. Trofim Lysenko believed that, given the right conditions,
a. rice would be more productive if loved
b. rye would turn into wheat
c. wheat would grow best if planted in clumps
d. scientists are most productive when exiled to Siberia
e. both b and c.
8. The following is not an assumption of the Hardy-Weinberg Law:
9. The following is not an aspect of science
a. Conclusions are provisional
b. Conclusions must support the null hypothesis
c. Conclusions, if important, will be tested by others and reversed if wrong
d. They are all aspects of science
e. None of them is an aspect of science.
10. The coexistence grasses of the Serengeti appears to depend on
a. urine
b. water
c. wildebeest
d. the interaction of all of the above
e. a and b.
11. Which of the following adaptations does not help to prevent water loss in plants. [SS]
a. Mid-day wilting
b. Low leaf area to root ratios
c. Thin cuticles
d. Few stomates
e. Spines or hairs on the plants surface
12. Plants adapt to arid climates and conserve water by which of the following methods: [SS]
a. long roots
b. states of dormancy
c. thick leaves
d. few stomata
e. all of the above
13. Which of the following is not a use for models [SS]
a. to generate hypotheses
b. to make predictions
c. to test hypotheses
d. all of the above are uses for models
True-False – circle T for true, F for false. Answer five (4 pts each; 20 pts total).
T F Natural selection, the most important mechanism leading to evolution, can be observed in our lifetime.
T F The extremely strong relationship between temperature and CO2 levels in the atmosphere over the past 160,000 years is proof that atmospheric CO2 drives climate.
T F Statistics are both procedures used to understand data and summary values of data.
T F "Population," in statistical sense, is the entire universe of interest.
T F Given the following data set {1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32} the best measure of central tendency is the mean.
T F The p-value is the probability that the null hypothesis is true.
T F In science we rarely prove the null hypothesis either true or false.
T F Fish and insects have no mechanisms to control their body temperature.
T F Dynamics of communities can be strongly influenced by variability at the genetic level.
T F A fish that lives in fresh water must drink.
T F The field guide discusses "indicator species." Those are species that indicate interesting aspects of communities.
Succinctly define or discuss
two of the following in the space provided. (5 pts each; 10 pts total)Niche Falsifiability
Null hypothesis Species
Science Disruptive selection
Inference Statistical significance
Counter-current exchange mechanism
Formation of the Hawaiian Islands
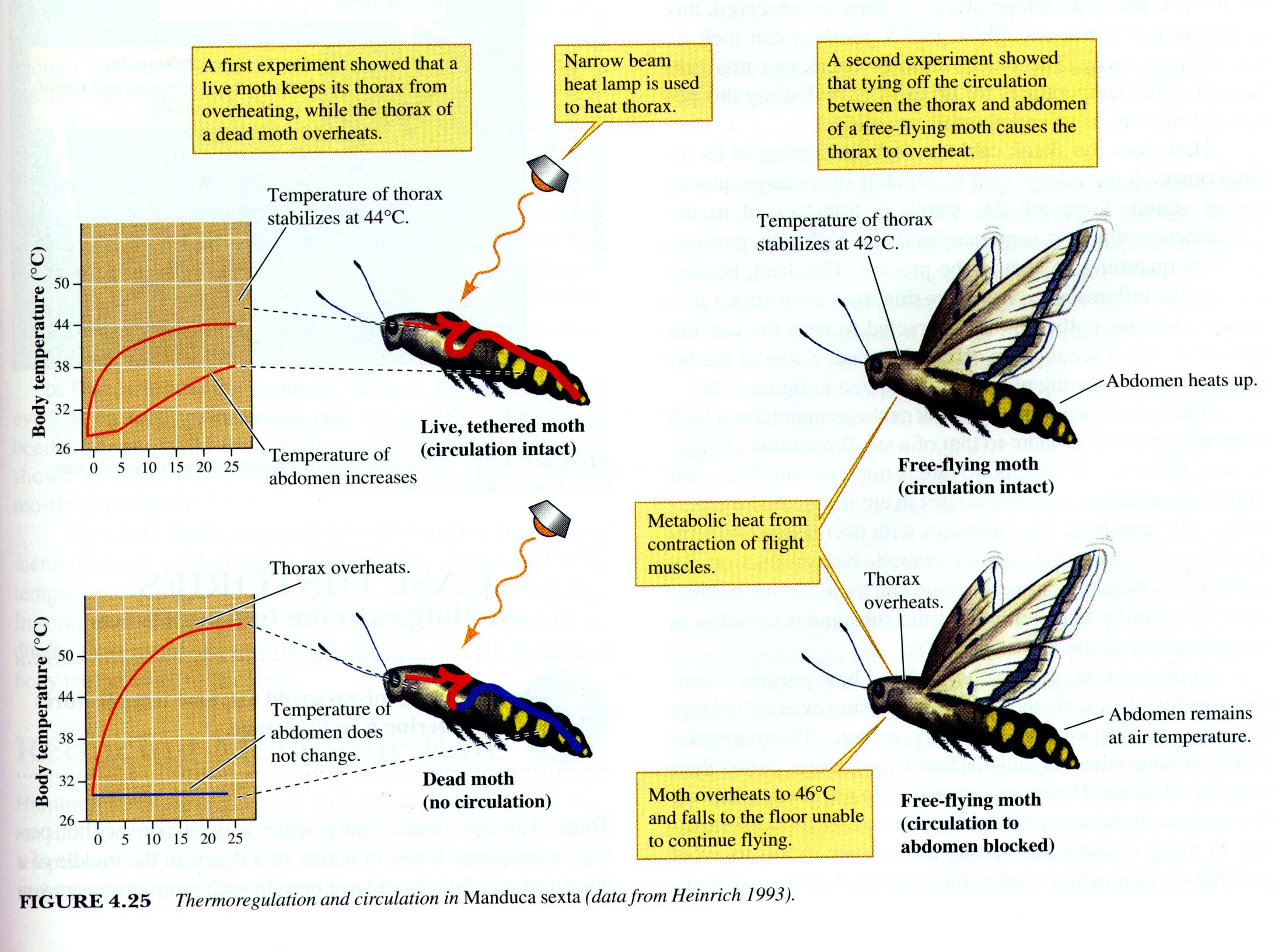
 1. In the figure
1. In the figure
on the right, Bernd
Heinrich conlcuded
what about these moths?
2. What are the four, easily observed characteristics of natural selection? Give sufficient detail to show you know and understand what they are.
3. Provide three reasons why we should build models in ecology. Explanations are not needed, please just identify the reasons to model.
4. Provide three reasons why birds migrate.
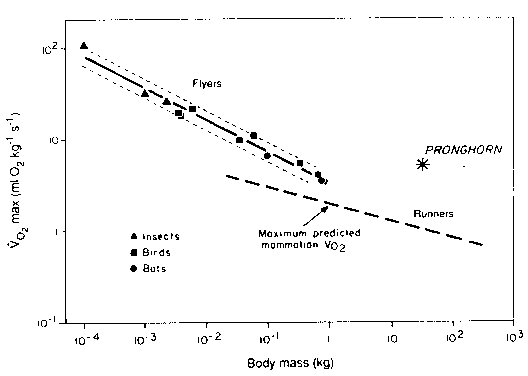
5. In the graph, pronghorn antelopes all alone in their oxygen consumption rates as a function of body mass. In the space provided, briefly explain the best going explanation for why this pattern exists.
Fill in the missing word or phrase for three of the following. (3 pts each, 9 total)
Design an experiment to test the following null hypothesis. You must provide a clearly labeled diagram of treatments. (10 pts)
Null hypothesis: Squirrel urine has no influence on tree growth rate (biomass accumulation per unit time).