| NAME | EPONYMOUS CONCEPT | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| Hamilton(ian) | operator | energy for quantum mechanics |
| Sommerfeld | model | semi-classical electrons in metals |
| Pauli | exclusion principle | one fermion per quantum state |
| Fermi | sphere | electrons in reciprocal space at 0K |
| Maxwell | distribution | statistics of classical particles |
| Fermi & Dirac | distribution | statistics of fermions |
| Madelung | rule | orbital filling order |
| Coulomb | law | electrical forces |
| ionic | bonding | due to atomic charge transfer |
| covalent | bonding | how quantum mechanics makes molecules |
| hydrogen | bonding | second weakest atomic attraction |
| van der Waals | force | fluctuating dipole interaction |
| Lennard-Jones | potential | 6th and 12th powers of distance |
| Taylor | expansion | all functions are a polynomials |
| Newton | law | fundamental classical dynamics rule |
| Nyquist | frequency | where aliasing starts |
| Brillouin | zone | un-aliased reciprocal space region |
| acoustic | branch | part of dispersion relation, always |
| optical | branch | part of dispersion relation, sometimes |
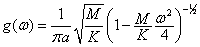
Concepts to know: