Misc
Problem Set 2 Solution
Available through Canvas
Colloquium
Dane Taylor, University of Buffalo
“Centrality Analysis for Time-Varying Social Networks (and Beyond)”
- A “network” is a system of objects connected by some relationship, e.g., people in a social network connected by “friend” relationships.
- “Centrality” deals with how important an object is for connecting others or other groups.
Thursday, Sept. 28, 4:00 - about 5:00 PM, Newton 203
Up to 2 problem set points of extra credit for going and writing a paragraph about some connection you make to the talk (for instance, a way it applies to something you’re interested in (mathematical or otherwise), something new you learned from it, a question it left you with, etc.)
- “Due” any time before I submit final grades in December.
Questions?
Grading Problem Set 3?
Schedule your meetings so that they’re over by 5:00 PM Wednesday.
The Product and Quotient Rules
The latter part of section 3.3
Examples
Example. Find dy/dx given that y = (x2 + 3x - 2)(x3 - 9).
Reading ideas: if j(x) = f(x)g(x), then j′(x) = f′(x)g(x) + g′(x)f(x).
The key part of setting this problem up is to recognize the f(x) and g(x) parts of the product. Then you can plug them into the right-hand side of the product rule.
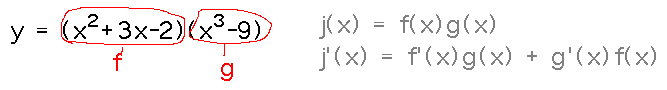
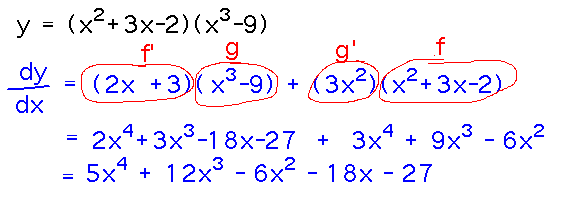
Example. Find dy/dx given that y = (6x9 - x3 + 17/x) (x2 + 6x - 7).
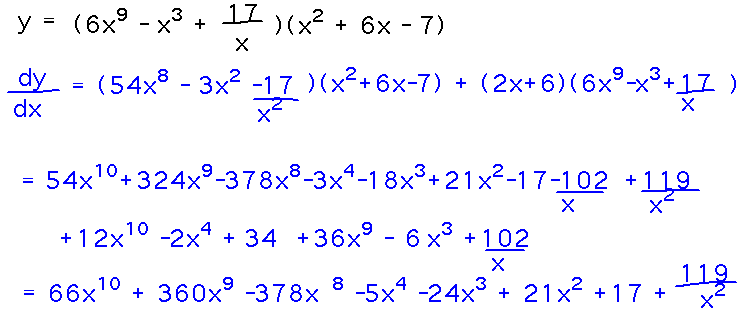
Take-Aways. Identify f and g, then plug them into product rule.
This works even when the resulting algebra is messy.
Example. Find h′(y) given that h(y) = (3y - 2) / (y2 + 6).
Reading idea: The quotient rule say h′(y) = (f′(y)g(y)-g′(y)f(y))/(g(y))2
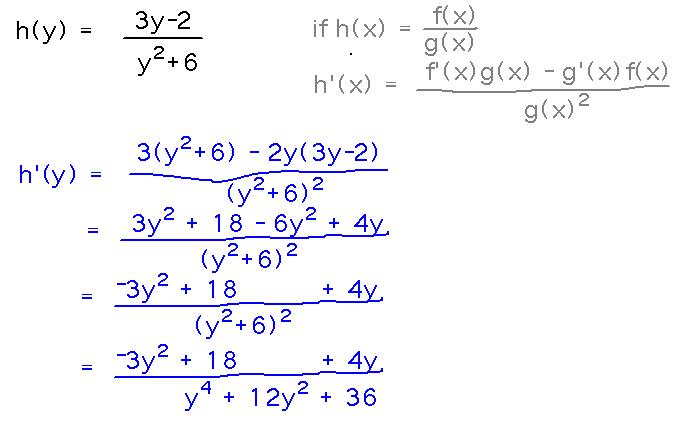
Example. Find dy/dx given that y = 5 / (2x-1)2
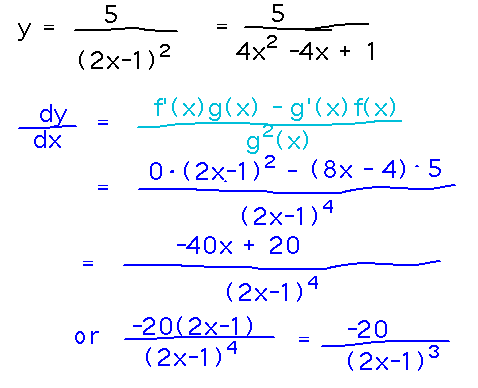
Take-Aways. Using the quotient rule also boils down to identifying f and g and then plugging them into the formula in the rule.
Sometimes it helps to use algebra to simply expressions before taking derivatives.
You can use the quotient rule to find derivatives of reciprocals. It becomes a little simpler in these uses because one of the terms in the numerator is 0.
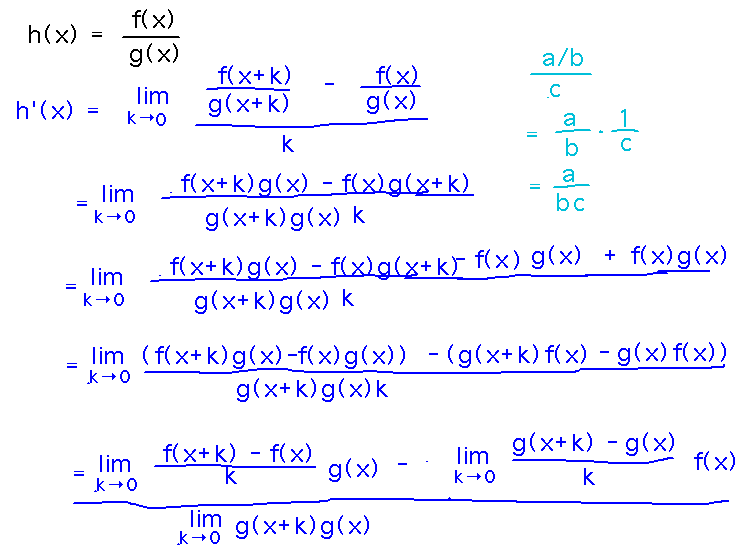
Prove the Quotient Rule
Reading Ideas. Use the limit definition of derivative.
Use the book’s proof of the product rule as a model or source of ideas.
The big-picture goal is to break the single limit that definition produces into 2 limits, one for each term in the numerator from the quotient rule. Or maybe even 3 limits: 2 for the numerator and the third for the denominator.
To break up the original limit, consider adding and then subtracting terms that will conveniently group with the terms already present to create derivatives of f and g.
Problem Set
See handout.
Next
Derivatives of trigonometric functions.
Read section 3.5 (for Thursday’s class).